The MATCH clause allows for full-text searches in text fields. The input query string is tokenized using the same settings applied to the text during indexing. In addition to the tokenization of input text, the query string supports a number of full-text operators that enforce various rules on how keywords should provide a valid match.
Full-text match clauses can be combined with attribute filters as an AND boolean. OR relations between full-text matches and attribute filters are not supported.
The match query is always executed first in the filtering process, followed by the attribute filters. The attribute filters are applied to the result set of the match query. A query without a match clause is called a fullscan.
There must be at most one MATCH() in the SELECT clause.
Using the full-text query syntax, matching is performed across all indexed text fields of a document, unless the expression requires a match within a field (like phrase search) or is limited by field operators.
When using JOIN queries, MATCH() can accept an optional second parameter that specifies which table the full-text search should be applied to. By default, the full-text query is applied to the left table in the JOIN operation:
SELECT * FROM table1 LEFT JOIN table2 ON table1.id = table2.id WHERE MATCH('search query', table2);This allows you to perform full-text searches on specific tables in a join operation. For more details on using MATCH with JOINs, see the Joining tables section.
MATCH('search query' [, table_name])'search query': The full-text search query string, which can include various full-text operators.table_name: (Optional) The name of the table to apply the full-text search to, used inJOINqueries to specify a different table than the default left table.
The SELECT statement uses a MATCH clause, which must come after WHERE, for performing full-text searches. MATCH() accepts an input string in which all full-text operators are available.
- SQL
- MATCH with filters
SELECT * FROM myindex WHERE MATCH('"find me fast"/2');An example of a more complex query using MATCH with WHERE filters.
SELECT * FROM myindex WHERE MATCH('cats|birds') AND (`title`='some title' AND `id`=123);+------+------+----------------+
| id | gid | title |
+------+------+----------------+
| 1 | 11 | first find me |
| 2 | 12 | second find me |
+------+------+----------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)Full-text matching is available in the /search endpoint and in HTTP-based clients. The following clauses can be used for performing full-text matches:
"match" is a simple query that matches the specified keywords in the specified fields.
"query":
{
"match": { "field": "keyword" }
}You can specify a list of fields:
"match":
{
"field1,field2": "keyword"
}Or you can use _all or * to search all fields.
You can search all fields except one using "!field":
"match":
{
"!field1": "keyword"
}By default, keywords are combined using the OR operator. However, you can change that behavior using the "operator" clause:
"query":
{
"match":
{
"content,title":
{
"query":"keyword",
"operator":"or"
}
}
}"operator" can be set to "or" or "and".
The boost modifier can also be applied. It raises the word IDF_score by the indicated factor in ranking scores that incorporate IDF into their calculations. It does not impact the matching process in any manner.
"query":
{
"match":
{
"field1":
{
"query": "keyword",
"boost": 2.0
}
}
}"match_phrase" is a query that matches the entire phrase. It is similar to a phrase operator in SQL. Here's an example:
"query":
{
"match_phrase": { "_all" : "had grown quite" }
}"query_string" accepts an input string as a full-text query in MATCH() syntax.
"query":
{
"query_string": "Church NOTNEAR/3 street"
}"match_all" accepts an empty object and returns documents from the table without performing any attribute filtering or full-text matching. Alternatively, you can just omit the query clause in the request which will have the same effect.
"query":
{
"match_all": {}
}All full-text match clauses can be combined with must, must_not, and should operators of a JSON bool query.
- match
- match_phrase
- query_string
- PHP
- Python
- Python-asyncio
- javascript
- Java
- C#
- Rust
- TypeScript
- Go
POST /search
-d
'{
"table" : "hn_small",
"query":
{
"match":
{
"*" : "find joe"
}
},
"_source": ["story_author","comment_author"],
"limit": 1
}'POST /search
-d
'{
"table" : "hn_small",
"query":
{
"match_phrase":
{
"*" : "find joe"
}
},
"_source": ["story_author","comment_author"],
"limit": 1
}'POST /search
-d
'{ "table" : "hn_small",
"query":
{
"query_string": "@comment_text \"find joe fast \"/2"
},
"_source": ["story_author","comment_author"],
"limit": 1
}'$search = new Search(new Client());
$result = $search->('@title find me fast');
foreach($result as $doc)
{
echo 'Document: '.$doc->getId();
foreach($doc->getData() as $field=>$value)
{
echo $field.': '.$value;
}
}searchApi.search({"table":"hn_small","query":{"query_string":"@comment_text \"find joe fast \"/2"}, "_source": ["story_author","comment_author"], "limit":1})await searchApi.search({"table":"hn_small","query":{"query_string":"@comment_text \"find joe fast \"/2"}, "_source": ["story_author","comment_author"], "limit":1})res = await searchApi.search({"table":"hn_small","query":{"query_string":"@comment_text \"find joe fast \"/2"}, "_source": ["story_author","comment_author"], "limit":1});query = new HashMap<String,Object>();
query.put("query_string", "@comment_text \"find joe fast \"/2");
searchRequest = new SearchRequest();
searchRequest.setIndex("hn_small");
searchRequest.setQuery(query);
searchRequest.addSourceItem("story_author");
searchRequest.addSourceItem("comment_author");
searchRequest.limit(1);
searchResponse = searchApi.search(searchRequest);object query = new { query_string="@comment_text \"find joe fast \"/2" };
var searchRequest = new SearchRequest("hn_small", query);
searchRequest.Source = new List<string> {"story_author", "comment_author"};
searchRequest.Limit = 1;
SearchResponse searchResponse = searchApi.Search(searchRequest);let query = SearchQuery {
query_string: Some(serde_json::json!("@comment_text \"find joe fast \"/2").into()),
..Default::default()
};
let search_req = SearchRequest {
table: "hn_small".to_string(),
query: Some(Box::new(query)),
source: serde_json::json!(["story_author", "comment_author"]),
limit: serde_json::json!(1),
..Default::default(),
};
let search_res = search_api.search(search_req).await;res = await searchApi.search({
index: 'test',
query: { query_string: "test document 1" },
"_source": ["content", "title"],
limit: 1
});searchRequest := manticoresearch.NewSearchRequest("test")
query := map[string]interface{} {"query_string": "test document 1"}
searchReq.SetSource([]string{"content", "title"})
searchReq.SetLimit(1)
resp, httpRes, err := search.SearchRequest(*searchRequest).Execute(){
"took" : 3,
"timed_out" : false,
"hits" : {
"hits" : [
{
"_id": 668018,
"_score" : 3579,
"_source" : {
"story_author" : "IgorPartola",
"comment_author" : "joe_the_user"
}
}
],
"total" : 88063,
"total_relation" : "eq"
}
}{
"took" : 3,
"timed_out" : false,
"hits" : {
"hits" : [
{
"_id": 807160,
"_score" : 2599,
"_source" : {
"story_author" : "rbanffy",
"comment_author" : "runjake"
}
}
],
"total" : 2,
"total_relation" : "eq"
}
}{
"took" : 3,
"timed_out" : false,
"hits" : {
"hits" : [
{
"_id": 807160,
"_score" : 2566,
"_source" : {
"story_author" : "rbanffy",
"comment_author" : "runjake"
}
}
],
"total" : 1864,
"total_relation" : "eq"
}
}Document: 1
title: first find me fast
gid: 11
Document: 2
title: second find me fast
gid: 12{'aggregations': None,
'hits': {'hits': [{'_id': '807160',
'_score': 2566,
'_source': {'comment_author': 'runjake',
'story_author': 'rbanffy'}}],
'max_score': None,
'total': 1864,
'total_relation': 'eq'},
'profile': None,
'timed_out': False,
'took': 2,
'warning': None}{'aggregations': None,
'hits': {'hits': [{'_id': '807160',
'_score': 2566,
'_source': {'comment_author': 'runjake',
'story_author': 'rbanffy'}}],
'max_score': None,
'total': 1864,
'total_relation': 'eq'},
'profile': None,
'timed_out': False,
'took': 2,
'warning': None}{
took: 1,
timed_out: false,
hits:
exports {
total: 1864,
total_relation: 'eq',
hits:
[ { _id: '807160',
_score: 2566,
_source: { story_author: 'rbanffy', comment_author: 'runjake' }
}
]
}
}class SearchResponse {
took: 1
timedOut: false
aggregations: null
hits: class SearchResponseHits {
maxScore: null
total: 1864
totalRelation: eq
hits: [{_id=807160, _score=2566, _source={story_author=rbanffy, comment_author=runjake}}]
}
profile: null
warning: null
}class SearchResponse {
took: 1
timedOut: false
aggregations: null
hits: class SearchResponseHits {
maxScore: null
total: 1864
totalRelation: eq
hits: [{_id=807160, _score=2566, _source={story_author=rbanffy, comment_author=runjake}}]
}
profile: null
warning: null
}class SearchResponse {
took: 1
timedOut: false
aggregations: null
hits: class SearchResponseHits {
maxScore: null
total: 1864
totalRelation: eq
hits: [{_id=807160, _score=2566, _source={story_author=rbanffy, comment_author=runjake}}]
}
profile: null
warning: null
}{
took: 1,
timed_out: false,
hits:
exports {
total: 5,
total_relation: 'eq',
hits:
[ { _id: '1',
_score: 2566,
_source: { content: 'This is a test document 1', title: 'Doc 1' }
}
]
}
}{
"hits": {
"hits": [
{
"_id": 1,
"_score": 2566,
"_source": {
"content": "This is a test document 1",
"title": "Doc 1"
}
}
],
"total": 5,
"total_relation": "eq"
},
"timed_out": false,
"took": 0
}The query string can include specific operators that define the conditions for how the words from the query string should be matched.
An implicit logical AND operator is always present, so "hello world" implies that both "hello" and "world" must be found in the matching document.
hello worldNote: There is no explicit AND operator.
The logical OR operator | has a higher precedence than AND, so looking for cat | dog | mouse means looking for (cat | dog | mouse) rather than (looking for cat) | dog | mouse.
hello | worldNote: There is no operator OR. Please use | instead.
hello MAYBE worldThe MAYBE operator functions similarly to the | operator, but it does not return documents that match only the right subtree expression.
hello -world
hello !worldThe negation operator enforces a rule for a word to not exist.
Queries containing only negations are not supported by default. To enable, use the server option not_terms_only_allowed.
@title hello @body worldThe field limit operator restricts subsequent searches to a specified field. By default, the query will fail with an error message if the given field name does not exist in the searched table. However, this behavior can be suppressed by specifying the @@relaxed option at the beginning of the query:
@@relaxed @nosuchfield my queryThis can be useful when searching through heterogeneous tables with different schemas.
Field position limits additionally constrain the search to the first N positions within a given field (or fields). For example, @body [50] hello will not match documents where the keyword hello appears at position 51 or later in the body.
@body[50] helloMultiple-field search operator:
@(title,body) hello worldIgnore field search operator (ignores any matches of 'hello world' from the 'title' field):
@!title hello worldIgnore multiple-field search operator (if there are fields 'title', 'subject', and 'body', then @!(title) is equivalent to @(subject,body)):
@!(title,body) hello worldAll-field search operator:
@* hello"hello world"The phrase operator mandates that the words be adjacent to each other.
The phrase search operator can include a match any term modifier. Within the phrase operator, terms are positionally significant. When the 'match any term' modifier is employed, the positions of the subsequent terms in that phrase query will be shifted. As a result, the 'match any' modifier does not affect search performance.
Note: When using this operator with queries containing more than 31 keywords, ranking statistics (such as tf, idf, bm25) for keywords at position 31 and above may be under-counted. This is due to a 32-bit mask used internally to track term occurrences within a match. Matching logic (finding documents) remains correct, but ranking scores may be affected for very long queries.
"exact * phrase * * for terms"You can also use the OR operator inside the quotes. The OR operator (|) must be enclosed in brackets () when used inside phrases. Each option is checked at the same position, and the phrase matches if any of the options fit that position.
Correct examples (with brackets):
"( a | b ) c"
"( ( a b c ) | d ) e"
"man ( happy | sad ) but all ( ( as good ) | ( as fast ) )"Incorrect examples (without brackets - these won't work):
"a | b c"
"happy | sad""hello world"~10Proximity distance is measured in words, accounting for word count, and applies to all words within quotes. For example, the query "cat dog mouse"~5 indicates that there must be a span of fewer than 8 words containing all 3 words. Therefore, a document with CAT aaa bbb ccc DOG eee fff MOUSE will not match this query, as the span is exactly 8 words long.
Note: When using this operator with queries containing more than 31 keywords, ranking statistics (such as tf, idf, bm25) for keywords at position 31 and above may be under-counted. This is due to a 32-bit mask used internally to track term occurrences within a match. Matching logic (finding documents) remains correct, but ranking scores may be affected for very long queries.
You can also use the OR operator inside a proximity search. The OR operator (|) must be enclosed in brackets () when used inside proximity searches. Each option is checked separately.
Correct example (with brackets):
"( two | four ) fish chips"~5Incorrect example (without brackets - this won't work):
"two | four fish chips"~5"the world is a wonderful place"/3The quorum matching operator introduces a type of fuzzy matching. It will match only those documents that meet a given threshold of specified words. In the example above ("the world is a wonderful place"/3), it will match all documents containing at least 3 of the 6 specified words. The operator is limited to 255 keywords. Instead of an absolute number, you can also provide a value between 0.0 and 1.0 (representing 0% and 100%), and Manticore will match only documents containing at least the specified percentage of the given words. The same example above could also be expressed as "the world is a wonderful place"/0.5, and it would match documents with at least 50% of the 6 words.
The quorum operator supports the OR (|) operator. The OR operator (|) must be enclosed in brackets () when used inside quorum matching. Only one word from each OR group counts toward the match.
Correct examples (with brackets):
"( ( a b c ) | d ) e f g"/0.5
"happy ( sad | angry ) man"/2Incorrect example (without brackets - this won't work):
"a b c | d e f g"/0.5aaa << bbb << cccThe strict order operator (also known as the "before" operator) matches a document only if its argument keywords appear in the document precisely in the order specified in the query. For example, the query black << cat will match the document "black and white cat" but not the document "that cat was black". The order operator has the lowest priority. It can be applied to both individual keywords and more complex expressions. For instance, this is a valid query:
(bag of words) << "exact phrase" << red|green|blueraining =cats and =dogs
="exact phrase"The exact form keyword modifier matches a document only if the keyword appears in the exact form specified. By default, a document is considered a match if the stemmed/lemmatized keyword matches. For instance, the query "runs" will match both a document containing "runs" and one containing "running", because both forms stem to just "run". However, the =runs query will only match the first document. The exact form modifier requires the index_exact_words option to be enabled.
Another use case is to prevent expanding a keyword to its *keyword* form. For example, with index_exact_words=1 + expand_keywords=1/star, bcd will find a document containing abcde, but =bcd will not.
As a modifier affecting the keyword, it can be used within operators such as phrase, proximity, and quorum operators. Applying an exact form modifier to the phrase operator is possible, and in this case, it internally adds the exact form modifier to all terms in the phrase.
nation* *nation* *nationalRequires min_infix_len for prefix (expansion in trail) and/or suffix (expansion in head). If only prefixing is desired, min_prefix_len can be used instead.
The search will attempt to find all expansions of the wildcarded tokens, and each expansion is recorded as a matched hit. The number of expansions for a token can be controlled with the expansion_limit table setting. Wildcarded tokens can have a significant impact on query search time, especially when tokens have short lengths. In such cases, it is desirable to use the expansion limit.
The wildcard operator can be automatically applied if the expand_keywords table setting is used.
In addition, the following inline wildcard operators are supported:
?can match any single character:t?stwill matchtest, but notteast%can match zero or one character:tes%will matchtesortest, but nottesting
The inline operators require dict=keywords (enabled by default) and prefixing/infixing enabled.
REGEX(/t.?e/)Requires the min_infix_len or min_prefix_len and dict=keywords options to be set (which is a default).
Similarly to the wildcard operators, the REGEX operator attempts to find all tokens matching the provided pattern, and each expansion is recorded as a matched hit. Note, this can have a significant impact on query search time, as the entire dictionary is scanned, and every term in the dictionary undergoes matching with the REGEX pattern.
The patterns should adhere to the RE2 syntax. The REGEX expression delimiter is the first symbol after the open bracket. In other words, all text between the open bracket followed by the delimiter and the delimiter and the closed bracket is considered as a RE2 expression.
Please note that the terms stored in the dictionary undergo charset_table transformation, meaning that for example, REGEX may not be able to match uppercase characters if all characters are lowercased according to the charset_table (which happens by default). To successfully match a term using a REGEX expression, the pattern must correspond to the entire token. To achieve partial matching, place .* at the beginning and/or end of your pattern.
REGEX(/.{3}t/)
REGEX(/t.*\d*/)^hello world$Field-start and field-end keyword modifiers ensure that a keyword only matches if it appears at the very beginning or the very end of a full-text field, respectively. For example, the query "^hello world$" (enclosed in quotes to combine the phrase operator with the start/end modifiers) will exclusively match documents containing at least one field with these two specific keywords.
boosted^1.234 boostedfieldend$^1.234The boost modifier raises the word IDF_score by the indicated factor in ranking scores that incorporate IDF into their calculations. It does not impact the matching process in any manner.
hello NEAR/3 world NEAR/4 "my test"The NEAR operator is a more generalized version of the proximity operator. Its syntax is NEAR/N, which is case-sensitive and does not allow spaces between the NEAR keywords, slash sign, and distance value.
While the original proximity operator works only on sets of keywords, NEAR is more versatile and can accept arbitrary subexpressions as its two arguments. It matches a document when both subexpressions are found within N words of each other, regardless of their order. NEAR is left-associative and shares the same (lowest) precedence as BEFORE.
It is important to note that one NEAR/7 two NEAR/7 three is not exactly equivalent to "one two three"~7. The key difference is that the proximity operator allows up to 6 non-matching words between all three matching words, while the version with NEAR is less restrictive: it permits up to 6 words between one and two, and then up to 6 more between that two-word match and three.
Note: When using this operator with queries containing more than 31 keywords, ranking statistics (such as tf, idf, bm25) for keywords at position 31 and above may be under-counted. This is due to a 32-bit mask used internally to track term occurrences within a match. Matching logic (finding documents) remains correct, but ranking scores may be affected for very long queries.
Church NOTNEAR/3 streetThe NOTNEAR operator serves as a negative assertion and functions as the logical inverse of the NEAR operator. It matches a document when the left argument is present, provided that the right argument is either absent from the document or is located more than the specified distance away from the left argument.
The syntax is NOTNEAR/N, which is case-sensitive and does not permit spaces between the NOTNEAR keyword, slash sign, and distance value.
Key behaviors include:
- Symmetry: Like
NEAR, theNOTNEARoperator applies regardless of the order of terms in the text. It will exclude a match if the right argument is found within the specified distance either before or after the left argument. - Distance Threshold: The distance
Nrepresents the nearby range (inclusive). If the words are separated byNwords or fewer, the match is discarded. The right argument must beN + 1or more words away. - Arguments: Both arguments of this operator can be terms, phrases, or groups of operators.
all SENTENCE words SENTENCE "in one sentence""Bill Gates" PARAGRAPH "Steve Jobs"The SENTENCE and PARAGRAPH operators match a document when both of their arguments are within the same sentence or the same paragraph of text, respectively. These arguments can be keywords, phrases, or instances of the same operator.
The order of the arguments within the sentence or paragraph is irrelevant. These operators function only with tables built with index_sp (sentence and paragraph indexing feature) enabled and revert to a simple AND operation otherwise. For information on what constitutes a sentence and a paragraph, refer to the index_sp directive documentation.
ZONE:(h3,h4)
only in these titlesThe ZONE limit operator closely resembles the field limit operator but limits matching to a specified in-field zone or a list of zones. It is important to note that subsequent subexpressions do not need to match within a single continuous span of a given zone and may match across multiple spans. For example, the query (ZONE:th hello world) will match the following sample document:
<th>Table 1. Local awareness of Hello Kitty brand.</th>
.. some table data goes here ..
<th>Table 2. World-wide brand awareness.</th>The ZONE operator affects the query until the next field or ZONE limit operator, or until the closing parenthesis. It functions exclusively with tables built with zone support (refer to index_zones) and will be disregarded otherwise.
ZONESPAN:(h2)
only in a (single) titleThe ZONESPAN limit operator resembles the ZONE operator but mandates that the match occurs within a single continuous span. In the example provided earlier, ZONESPAN:th hello world would not match the document, as "hello" and "world" do not appear within the same span.
Since certain characters function as operators in the query string, they must be escaped to prevent query errors or unintended matching conditions.
The following characters should be escaped using a backslash (\):
! " $ ' ( ) - / < @ \ ^ | ~To escape a single quote ('), use one backslash:
SELECT * FROM your_index WHERE MATCH('l\'italiano');For the other characters in the list mentioned earlier, which are operators or query constructs, they must be treated as simple characters by the engine, with a preceding escape character. The backslash must also be escaped, resulting in two backslashes:
SELECT * FROM your_index WHERE MATCH('r\\&b | \\(official video\\)');To use a backslash as a character, you must escape both the backslash as a character and the backslash as the escape operator, which requires four backslashes:
SELECT * FROM your_index WHERE MATCH('\\\\ABC');When you are working with JSON data in Manticore Search and need to include a double quote (") within a JSON string, it's important to handle it with proper escaping. In JSON, a double quote within a string is escaped using a backslash (\). However, when inserting the JSON data through an SQL query, Manticore Search interprets the backslash (\) as an escape character within strings.
To ensure the double quote is correctly inserted into the JSON data, you need to escape the backslash itself. This results in using two backslashes (\\) before the double quote. For example:
insert into tbl(j) values('{"a": "\\"abc\\""}');MySQL drivers provide escaping functions (e.g., mysqli_real_escape_string in PHP or conn.escape_string in Python), but they only escape specific characters.
You will still need to add escaping for the characters from the previously mentioned list that are not escaped by their respective functions.
Because these functions will escape the backslash for you, you only need to add one backslash.
This also applies to drivers that support (client-side) prepared statements. For example, with PHP PDO prepared statements, you need to add a backslash for the $ character:
$statement = $ln_sph->prepare( "SELECT * FROM index WHERE MATCH(:match)");
$match = '\$manticore';
$statement->bindParam(':match',$match,PDO::PARAM_STR);
$results = $statement->execute();This results in the final query SELECT * FROM index WHERE MATCH('\\$manticore');
The same rules for the SQL protocol apply, with the exception that for JSON, the double quote must be escaped with a single backslash, while the rest of the characters require double escaping.
When using JSON libraries or functions that convert data structures to JSON strings, the double quote and single backslash are automatically escaped by these functions and do not need to be explicitly escaped.
The official clients utilize common JSON libraries/functions available in their respective programming languages under the hood. The same rules for escaping mentioned earlier apply.
The asterisk (*) is a unique character that serves two purposes:
- as a wildcard prefix/suffix expander
- as an any-term modifier within a phrase search.
Unlike other special characters that function as operators, the asterisk cannot be escaped when it's in a position to provide one of its functionalities.
In non-wildcard queries, the asterisk does not require escaping, whether it's in the charset_table or not.
In wildcard queries, an asterisk in the middle of a word does not require escaping. As a wildcard operator (either at the beginning or end of the word), the asterisk will always be interpreted as the wildcard operator, even if escaping is applied.
To escape special characters in JSON nodes, use a backtick. For example:
MySQL [(none)]> select * from t where json.`a=b`=234;
+---------------------+-------------+------+
| id | json | text |
+---------------------+-------------+------+
| 8215557549554925578 | {"a=b":234} | |
+---------------------+-------------+------+
MySQL [(none)]> select * from t where json.`a:b`=123;
+---------------------+-------------+------+
| id | json | text |
+---------------------+-------------+------+
| 8215557549554925577 | {"a:b":123} | |
+---------------------+-------------+------+Consider this complex query example:
"hello world" @title "example program"~5 @body python -(php|perl) @* codeThe full meaning of this search is:
- Locate the words 'hello' and 'world' adjacently in any field within a document;
- Additionally, the same document must also contain the words 'example' and 'program' in the title field, with up to, but not including, 5 words between them; (For instance, "example PHP program" would match, but "example script to introduce outside data into the correct context for your program" would not, as there are 5 or more words between the two terms)
- Furthermore, the same document must have the word 'python' in the body field, while excluding 'php' or 'perl';
- Finally, the same document must include the word 'code' in any field.
The OR operator takes precedence over AND, so "looking for cat | dog | mouse" means "looking for (cat | dog | mouse)" rather than "(looking for cat) | dog | mouse".
To comprehend how a query will be executed, Manticore Search provides query profiling tools to examine the query tree generated by a query expression.
To enable full-text query profiling with an SQL statement, you must activate it before executing the desired query:
SET profiling =1;
SELECT * FROM test WHERE MATCH('@title abc* @body hey');To view the query tree, execute the SHOW PLAN command immediately after running the query:
SHOW PLAN;This command will return the structure of the executed query. Keep in mind that the 3 statements - SET profiling, the query, and SHOW - must be executed within the same session.
When using the HTTP JSON protocol we can just enable "profile":true to get in response the full-text query tree structure.
{
"table":"test",
"profile":true,
"query":
{
"match_phrase": { "_all" : "had grown quite" }
}
}The response will include a profile object containing a query member.
The query property holds the transformed full-text query tree. Each node consists of:
type: node type, which can be AND, OR, PHRASE, KEYWORD, etc.description: query subtree for this node represented as a string (inSHOW PLANformat)children: any child nodes, if presentmax_field_pos: maximum position within a field
A keyword node will additionally include:
word: the transformed keyword.querypos: position of this keyword in the query.excluded: keyword excluded from the query.expanded: keyword added by prefix expansion.field_start: keyword must appear at the beginning of the field.field_end: keyword must appear at the end of the field.boost: the keyword's IDF will be multiplied by this value.
- SQL
- JSON
- PHP
- Python
- Python-asyncio
- javascript
- Java
- C#
- Rust
- TypeScript
- Go
SET profiling=1;
SELECT * FROM test WHERE MATCH('@title abc* @body hey');
SHOW PLAN \GPOST /search
{
"table": "forum",
"query": {"query_string": "i me"},
"_source": { "excludes":["*"] },
"limit": 1,
"profile":true
}$result = $index->search('i me')->setSource(['excludes'=>['*']])->setLimit(1)->profile()->get();
print_r($result->getProfile());searchApi.search({"table":"forum","query":{"query_string":"i me"},"_source":{"excludes":["*"]},"limit":1,"profile":True})await searchApi.search({"table":"forum","query":{"query_string":"i me"},"_source":{"excludes":["*"]},"limit":1,"profile":True})res = await searchApi.search({"table":"forum","query":{"query_string":"i me"},"_source":{"excludes":["*"]},"limit":1,"profile":true});query = new HashMap<String,Object>();
query.put("query_string","i me");
searchRequest = new SearchRequest();
searchRequest.setIndex("forum");
searchRequest.setQuery(query);
searchRequest.setProfile(true);
searchRequest.setLimit(1);
searchRequest.setSort(new ArrayList<String>(){{
add("*");
}});
searchResponse = searchApi.search(searchRequest);object query = new { query_string="i me" };
var searchRequest = new SearchRequest("forum", query);
searchRequest.Profile = true;
searchRequest.Limit = 1;
searchRequest.Sort = new List<Object> { "*" };
var searchResponse = searchApi.Search(searchRequest);let query = SearchQuery {
query_string: Some(serde_json::json!("i me").into()),
..Default::default()
};
let search_req = SearchRequest {
table: "forum".to_string(),
query: Some(Box::new(query)),
sort: serde_json::json!(["*"]),
limit: serde_json::json!(1),
profile: serde_json::json!(true),
..Default::default(),
};
let search_res = search_api.search(search_req).await;res = await searchApi.search({
index: 'test',
query: { query_string: 'Text' },
_source: { excludes: ['*'] },
limit: 1,
profile: true
});searchRequest := manticoresearch.NewSearchRequest("test")
query := map[string]interface{} {"query_string": "Text"}
source := map[string]interface{} { "excludes": []string {"*"} }
searchRequest.SetQuery(query)
searchRequest.SetSource(source)
searchReq.SetLimit(1)
searchReq.SetProfile(true)
res, _, _ := apiClient.SearchAPI.Search(context.Background()).SearchRequest(*searchRequest).Execute()*************************** 1\. row ***************************
Variable: transformed_tree
Value: AND(
OR(fields=(title), KEYWORD(abcx, querypos=1, expanded), KEYWORD(abcm, querypos=1, expanded)),
AND(fields=(body), KEYWORD(hey, querypos=2)))
1 row in set (0.00 sec){
"took":1503,
"timed_out":false,
"hits":
{
"total":406301,
"hits":
[
{
"_id": 406443,
"_score":3493,
"_source":{}
}
]
},
"profile":
{
"query":
{
"type":"AND",
"description":"AND( AND(KEYWORD(i, querypos=1)), AND(KEYWORD(me, querypos=2)))",
"children":
[
{
"type":"AND",
"description":"AND(KEYWORD(i, querypos=1))",
"children":
[
{
"type":"KEYWORD",
"word":"i",
"querypos":1
}
]
},
{
"type":"AND",
"description":"AND(KEYWORD(me, querypos=2))",
"children":
[
{
"type":"KEYWORD",
"word":"me",
"querypos":2
}
]
}
]
}
}
}Array
(
[query] => Array
(
[type] => AND
[description] => AND( AND(KEYWORD(i, querypos=1)), AND(KEYWORD(me, querypos=2)))
[children] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[type] => AND
[description] => AND(KEYWORD(i, querypos=1))
[children] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[type] => KEYWORD
[word] => i
[querypos] => 1
)
)
)
[1] => Array
(
[type] => AND
[description] => AND(KEYWORD(me, querypos=2))
[children] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[type] => KEYWORD
[word] => me
[querypos] => 2
)
)
)
)
)
){'hits': {'hits': [{u'_id': u'100', u'_score': 2500, u'_source': {}}],
'total': 1},
'profile': {u'query': {u'children': [{u'children': [{u'querypos': 1,
u'type': u'KEYWORD',
u'word': u'i'}],
u'description': u'AND(KEYWORD(i, querypos=1))',
u'type': u'AND'},
{u'children': [{u'querypos': 2,
u'type': u'KEYWORD',
u'word': u'me'}],
u'description': u'AND(KEYWORD(me, querypos=2))',
u'type': u'AND'}],
u'description': u'AND( AND(KEYWORD(i, querypos=1)), AND(KEYWORD(me, querypos=2)))',
u'type': u'AND'}},
'timed_out': False,
'took': 0}{'hits': {'hits': [{u'_id': u'100', u'_score': 2500, u'_source': {}}],
'total': 1},
'profile': {u'query': {u'children': [{u'children': [{u'querypos': 1,
u'type': u'KEYWORD',
u'word': u'i'}],
u'description': u'AND(KEYWORD(i, querypos=1))',
u'type': u'AND'},
{u'children': [{u'querypos': 2,
u'type': u'KEYWORD',
u'word': u'me'}],
u'description': u'AND(KEYWORD(me, querypos=2))',
u'type': u'AND'}],
u'description': u'AND( AND(KEYWORD(i, querypos=1)), AND(KEYWORD(me, querypos=2)))',
u'type': u'AND'}},
'timed_out': False,
'took': 0}{"hits": {"hits": [{"_id": 100, "_score": 2500, "_source": {}}],
"total": 1},
"profile": {"query": {"children": [{"children": [{"querypos": 1,
"type": "KEYWORD",
"word": "i"}],
"description": "AND(KEYWORD(i, querypos=1))",
"type": "AND"},
{"children": [{"querypos": 2,
"type": "KEYWORD",
"word": "me"}],
"description": "AND(KEYWORD(me, querypos=2))",
"type": "AND"}],
"description": "AND( AND(KEYWORD(i, querypos=1)), AND(KEYWORD(me, querypos=2)))",
"type": "AND"}},
"timed_out": False,
"took": 0}class SearchResponse {
took: 18
timedOut: false
hits: class SearchResponseHits {
total: 1
hits: [{_id=100, _score=2500, _source={}}]
aggregations: null
}
profile: {query={type=AND, description=AND( AND(KEYWORD(i, querypos=1)), AND(KEYWORD(me, querypos=2))), children=[{type=AND, description=AND(KEYWORD(i, querypos=1)), children=[{type=KEYWORD, word=i, querypos=1}]}, {type=AND, description=AND(KEYWORD(me, querypos=2)), children=[{type=KEYWORD, word=me, querypos=2}]}]}}
}class SearchResponse {
took: 18
timedOut: false
hits: class SearchResponseHits {
total: 1
hits: [{_id=100, _score=2500, _source={}}]
aggregations: null
}
profile: {query={type=AND, description=AND( AND(KEYWORD(i, querypos=1)), AND(KEYWORD(me, querypos=2))), children=[{type=AND, description=AND(KEYWORD(i, querypos=1)), children=[{type=KEYWORD, word=i, querypos=1}]}, {type=AND, description=AND(KEYWORD(me, querypos=2)), children=[{type=KEYWORD, word=me, querypos=2}]}]}}
}class SearchResponse {
took: 18
timedOut: false
hits: class SearchResponseHits {
total: 1
hits: [{_id=100, _score=2500, _source={}}]
aggregations: null
}
profile: {query={type=AND, description=AND( AND(KEYWORD(i, querypos=1)), AND(KEYWORD(me, querypos=2))), children=[{type=AND, description=AND(KEYWORD(i, querypos=1)), children=[{type=KEYWORD, word=i, querypos=1}]}, {type=AND, description=AND(KEYWORD(me, querypos=2)), children=[{type=KEYWORD, word=me, querypos=2}]}]}}
}{
"hits":
{
"hits":
[{
"_id": 1,
"_score": 1480,
"_source": {}
}],
"total": 1
},
"profile":
{
"query": {
"children":
[{
"children":
[{
"querypos": 1,
"type": "KEYWORD",
"word": "i"
}],
"description": "AND(KEYWORD(i, querypos=1))",
"type": "AND"
},
{
"children":
[{
"querypos": 2,
"type": "KEYWORD",
"word": "me"
}],
"description": "AND(KEYWORD(me, querypos=2))",
"type": "AND"
}],
"description": "AND( AND(KEYWORD(i, querypos=1)), AND(KEYWORD(me, querypos=2)))",
"type": "AND"
}
},
"timed_out": False,
"took": 0
}{
"hits":
{
"hits":
[{
"_id": 1,
"_score": 1480,
"_source": {}
}],
"total": 1
},
"profile":
{
"query": {
"children":
[{
"children":
[{
"querypos": 1,
"type": "KEYWORD",
"word": "i"
}],
"description": "AND(KEYWORD(i, querypos=1))",
"type": "AND"
},
{
"children":
[{
"querypos": 2,
"type": "KEYWORD",
"word": "me"
}],
"description": "AND(KEYWORD(me, querypos=2))",
"type": "AND"
}],
"description": "AND( AND(KEYWORD(i, querypos=1)), AND(KEYWORD(me, querypos=2)))",
"type": "AND"
}
},
"timed_out": False,
"took": 0
}In some instances, the evaluated query tree may significantly differ from the original one due to expansions and other transformations.
- SQL
- JSON
- PHP
- Python
- Python-asyncio
- javascript
- Java
- C#
- Rust
- TypeScript
- Go
SET profiling=1;
SELECT id FROM forum WHERE MATCH('@title way* @content hey') LIMIT 1;
SHOW PLAN;POST /search
{
"table": "forum",
"query": {"query_string": "@title way* @content hey"},
"_source": { "excludes":["*"] },
"limit": 1,
"profile":true
}$result = $index->search('@title way* @content hey')->setSource(['excludes'=>['*']])->setLimit(1)->profile()->get();
print_r($result->getProfile());searchApi.search({"table":"forum","query":{"query_string":"@title way* @content hey"},"_source":{"excludes":["*"]},"limit":1,"profile":true})await searchApi.search({"table":"forum","query":{"query_string":"@title way* @content hey"},"_source":{"excludes":["*"]},"limit":1,"profile":true})res = await searchApi.search({"table":"forum","query":{"query_string":"@title way* @content hey"},"_source":{"excludes":["*"]},"limit":1,"profile":true});query = new HashMap<String,Object>();
query.put("query_string","@title way* @content hey");
searchRequest = new SearchRequest();
searchRequest.setIndex("forum");
searchRequest.setQuery(query);
searchRequest.setProfile(true);
searchRequest.setLimit(1);
searchRequest.setSort(new ArrayList<String>(){{
add("*");
}});
searchResponse = searchApi.search(searchRequest);object query = new { query_string="@title way* @content hey" };
var searchRequest = new SearchRequest("forum", query);
searchRequest.Profile = true;
searchRequest.Limit = 1;
searchRequest.Sort = new List<Object> { "*" };
var searchResponse = searchApi.Search(searchRequest);let query = SearchQuery {
query_string: Some(serde_json::json!("@title way* @content hey").into()),
..Default::default()
};
let search_req = SearchRequest {
table: "forum".to_string(),
query: Some(Box::new(query)),
sort: serde_json::json!(["*"]),
limit: serde_json::json!(1),
profile: serde_json::json!(true),
..Default::default(),
};
let search_res = search_api.search(search_req).await;res = await searchApi.search({
index: 'test',
query: { query_string: '@content 1'},
_source: { excludes: ["*"] },
limit:1,
profile":true
});searchRequest := manticoresearch.NewSearchRequest("test")
query := map[string]interface{} {"query_string": "1*"}
source := map[string]interface{} { "excludes": []string {"*"} }
searchRequest.SetQuery(query)
searchRequest.SetSource(source)
searchReq.SetLimit(1)
searchReq.SetProfile(true)
res, _, _ := apiClient.SearchAPI.Search(context.Background()).SearchRequest(*searchRequest).Execute()Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
+--------+
| id |
+--------+
| 711651 |
+--------+
1 row in set (0.04 sec)
+------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Variable | Value |
+------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| transformed_tree | AND(
OR(
OR(
AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(wayne, querypos=1, expanded)),
OR(
AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(ways, querypos=1, expanded)),
AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(wayyy, querypos=1, expanded)))),
AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way, querypos=1, expanded)),
OR(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way*, querypos=1, expanded))),
AND(fields=(content), KEYWORD(hey, querypos=2))) |
+------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec){
"took":33,
"timed_out":false,
"hits":
{
"total":105,
"hits":
[
{
"_id": 711651,
"_score":2539,
"_source":{}
}
]
},
"profile":
{
"query":
{
"type":"AND",
"description":"AND( OR( OR( AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(wayne, querypos=1, expanded)), OR( AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(ways, querypos=1, expanded)), AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(wayyy, querypos=1, expanded)))), AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way, querypos=1, expanded)), OR(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way*, querypos=1, expanded))), AND(fields=(content), KEYWORD(hey, querypos=2)))",
"children":
[
{
"type":"OR",
"description":"OR( OR( AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(wayne, querypos=1, expanded)), OR( AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(ways, querypos=1, expanded)), AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(wayyy, querypos=1, expanded)))), AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way, querypos=1, expanded)), OR(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way*, querypos=1, expanded)))",
"children":
[
{
"type":"OR",
"description":"OR( AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(wayne, querypos=1, expanded)), OR( AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(ways, querypos=1, expanded)), AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(wayyy, querypos=1, expanded))))",
"children":
[
{
"type":"AND",
"description":"AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(wayne, querypos=1, expanded))",
"fields":["title"],
"max_field_pos":0,
"children":
[
{
"type":"KEYWORD",
"word":"wayne",
"querypos":1,
"expanded":true
}
]
},
{
"type":"OR",
"description":"OR( AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(ways, querypos=1, expanded)), AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(wayyy, querypos=1, expanded)))",
"children":
[
{
"type":"AND",
"description":"AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(ways, querypos=1, expanded))",
"fields":["title"],
"max_field_pos":0,
"children":
[
{
"type":"KEYWORD",
"word":"ways",
"querypos":1,
"expanded":true
}
]
},
{
"type":"AND",
"description":"AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(wayyy, querypos=1, expanded))",
"fields":["title"],
"max_field_pos":0,
"children":
[
{
"type":"KEYWORD",
"word":"wayyy",
"querypos":1,
"expanded":true
}
]
}
]
}
]
},
{
"type":"AND",
"description":"AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way, querypos=1, expanded))",
"fields":["title"],
"max_field_pos":0,
"children":
[
{
"type":"KEYWORD",
"word":"way",
"querypos":1,
"expanded":true
}
]
},
{
"type":"OR",
"description":"OR(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way*, querypos=1, expanded))",
"fields":["title"],
"max_field_pos":0,
"children":
[
{
"type":"KEYWORD",
"word":"way*",
"querypos":1,
"expanded":true
}
]
}
]
},
{
"type":"AND",
"description":"AND(fields=(content), KEYWORD(hey, querypos=2))",
"fields":["content"],
"max_field_pos":0,
"children":
[
{
"type":"KEYWORD",
"word":"hey",
"querypos":2
}
]
}
]
}
}
}Array
(
[query] => Array
(
[type] => AND
[description] => AND( OR( OR( AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(wayne, querypos=1, expanded)), OR( AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(ways, querypos=1, expanded)), AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(wayyy, querypos=1, expanded)))), AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way, querypos=1, expanded)), OR(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way*, querypos=1, expanded))), AND(fields=(content), KEYWORD(hey, querypos=2)))
[children] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[type] => OR
[description] => OR( OR( AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(wayne, querypos=1, expanded)), OR( AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(ways, querypos=1, expanded)), AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(wayyy, querypos=1, expanded)))), AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way, querypos=1, expanded)), OR(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way*, querypos=1, expanded)))
[children] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[type] => OR
[description] => OR( AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(wayne, querypos=1, expanded)), OR( AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(ways, querypos=1, expanded)), AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(wayyy, querypos=1, expanded))))
[children] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[type] => AND
[description] => AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(wayne, querypos=1, expanded))
[fields] => Array
(
[0] => title
)
[max_field_pos] => 0
[children] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[type] => KEYWORD
[word] => wayne
[querypos] => 1
[expanded] => 1
)
)
)
[1] => Array
(
[type] => OR
[description] => OR( AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(ways, querypos=1, expanded)), AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(wayyy, querypos=1, expanded)))
[children] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[type] => AND
[description] => AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(ways, querypos=1, expanded))
[fields] => Array
(
[0] => title
)
[max_field_pos] => 0
[children] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[type] => KEYWORD
[word] => ways
[querypos] => 1
[expanded] => 1
)
)
)
[1] => Array
(
[type] => AND
[description] => AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(wayyy, querypos=1, expanded))
[fields] => Array
(
[0] => title
)
[max_field_pos] => 0
[children] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[type] => KEYWORD
[word] => wayyy
[querypos] => 1
[expanded] => 1
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
[1] => Array
(
[type] => AND
[description] => AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way, querypos=1, expanded))
[fields] => Array
(
[0] => title
)
[max_field_pos] => 0
[children] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[type] => KEYWORD
[word] => way
[querypos] => 1
[expanded] => 1
)
)
)
[2] => Array
(
[type] => OR
[description] => OR(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way*, querypos=1, expanded))
[fields] => Array
(
[0] => title
)
[max_field_pos] => 0
[children] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[type] => KEYWORD
[word] => way*
[querypos] => 1
[expanded] => 1
)
)
)
)
)
[1] => Array
(
[type] => AND
[description] => AND(fields=(content), KEYWORD(hey, querypos=2))
[fields] => Array
(
[0] => content
)
[max_field_pos] => 0
[children] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[type] => KEYWORD
[word] => hey
[querypos] => 2
)
)
)
)
)
){'hits': {'hits': [{u'_id': u'2811025403043381551',
u'_score': 2643,
u'_source': {}}],
'total': 1},
'profile': {u'query': {u'children': [{u'children': [{u'expanded': True,
u'querypos': 1,
u'type': u'KEYWORD',
u'word': u'way*'}],
u'description': u'AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way*, querypos=1, expanded))',
u'fields': [u'title'],
u'type': u'AND'},
{u'children': [{u'querypos': 2,
u'type': u'KEYWORD',
u'word': u'hey'}],
u'description': u'AND(fields=(content), KEYWORD(hey, querypos=2))',
u'fields': [u'content'],
u'type': u'AND'}],
u'description': u'AND( AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way*, querypos=1, expanded)), AND(fields=(content), KEYWORD(hey, querypos=2)))',
u'type': u'AND'}},
'timed_out': False,
'took': 0}{'hits': {'hits': [{u'_id': u'2811025403043381551',
u'_score': 2643,
u'_source': {}}],
'total': 1},
'profile': {u'query': {u'children': [{u'children': [{u'expanded': True,
u'querypos': 1,
u'type': u'KEYWORD',
u'word': u'way*'}],
u'description': u'AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way*, querypos=1, expanded))',
u'fields': [u'title'],
u'type': u'AND'},
{u'children': [{u'querypos': 2,
u'type': u'KEYWORD',
u'word': u'hey'}],
u'description': u'AND(fields=(content), KEYWORD(hey, querypos=2))',
u'fields': [u'content'],
u'type': u'AND'}],
u'description': u'AND( AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way*, querypos=1, expanded)), AND(fields=(content), KEYWORD(hey, querypos=2)))',
u'type': u'AND'}},
'timed_out': False,
'took': 0}{"hits": {"hits": [{"_id": 2811025403043381551,
"_score": 2643,
"_source": {}}],
"total": 1},
"profile": {"query": {"children": [{"children": [{"expanded": True,
"querypos": 1,
"type": "KEYWORD",
"word": "way*"}],
"description": "AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way*, querypos=1, expanded))",
"fields": ["title"],
"type": "AND"},
{"children": [{"querypos": 2,
"type": "KEYWORD",
"word": "hey"}],
"description": "AND(fields=(content), KEYWORD(hey, querypos=2))",
"fields": ["content"],
"type": "AND"}],
"description": "AND( AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way*, querypos=1, expanded)), AND(fields=(content), KEYWORD(hey, querypos=2)))",
"type": "AND"}},
"timed_out": False,
"took": 0}class SearchResponse {
took: 18
timedOut: false
hits: class SearchResponseHits {
total: 1
hits: [{_id=2811025403043381551, _score=2643, _source={}}]
aggregations: null
}
profile: {query={type=AND, description=AND( AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way*, querypos=1, expanded)), AND(fields=(content), KEYWORD(hey, querypos=2))), children=[{type=AND, description=AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way*, querypos=1, expanded)), fields=[title], children=[{type=KEYWORD, word=way*, querypos=1, expanded=true}]}, {type=AND, description=AND(fields=(content), KEYWORD(hey, querypos=2)), fields=[content], children=[{type=KEYWORD, word=hey, querypos=2}]}]}}
}class SearchResponse {
took: 18
timedOut: false
hits: class SearchResponseHits {
total: 1
hits: [{_id=2811025403043381551, _score=2643, _source={}}]
aggregations: null
}
profile: {query={type=AND, description=AND( AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way*, querypos=1, expanded)), AND(fields=(content), KEYWORD(hey, querypos=2))), children=[{type=AND, description=AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way*, querypos=1, expanded)), fields=[title], children=[{type=KEYWORD, word=way*, querypos=1, expanded=true}]}, {type=AND, description=AND(fields=(content), KEYWORD(hey, querypos=2)), fields=[content], children=[{type=KEYWORD, word=hey, querypos=2}]}]}}
}class SearchResponse {
took: 18
timedOut: false
hits: class SearchResponseHits {
total: 1
hits: [{_id=2811025403043381551, _score=2643, _source={}}]
aggregations: null
}
profile: {query={type=AND, description=AND( AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way*, querypos=1, expanded)), AND(fields=(content), KEYWORD(hey, querypos=2))), children=[{type=AND, description=AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way*, querypos=1, expanded)), fields=[title], children=[{type=KEYWORD, word=way*, querypos=1, expanded=true}]}, {type=AND, description=AND(fields=(content), KEYWORD(hey, querypos=2)), fields=[content], children=[{type=KEYWORD, word=hey, querypos=2}]}]}}
}{
"hits":
{
"hits":
[{
"_id": 1,
"_score": 1480,
"_source": {}
}],
"total": 1
},
"profile":
{
"query":
{
"children":
[{
"children":
[{
"expanded": True,
"querypos": 1,
"type": "KEYWORD",
"word": "1*"
}],
"description": "AND(fields=(content), KEYWORD(1*, querypos=1, expanded))",
"fields": ["content"],
"type": "AND"
}],
"description": "AND(fields=(content), KEYWORD(1*, querypos=1))",
"type": "AND"
}},
"timed_out": False,
"took": 0
}{
"hits":
{
"hits":
[{
"_id": 1,
"_score": 1480,
"_source": {}
}],
"total": 1
},
"profile":
{
"query":
{
"children":
[{
"children":
[{
"expanded": True,
"querypos": 1,
"type": "KEYWORD",
"word": "1*"
}],
"description": "AND(fields=(content), KEYWORD(1*, querypos=1, expanded))",
"fields": ["content"],
"type": "AND"
}],
"description": "AND(fields=(content), KEYWORD(1*, querypos=1))",
"type": "AND"
}},
"timed_out": False,
"took": 0
}The SQL statement EXPLAIN QUERY enables the display of the execution tree for a given full-text query without performing an actual search query on the table.
- SQL
EXPLAIN QUERY index_base '@title running @body dog'\G EXPLAIN QUERY index_base '@title running @body dog'\G
*************************** 1\. row ***************************
Variable: transformed_tree
Value: AND(
OR(
AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(run, querypos=1, morphed)),
AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(running, querypos=1, morphed))))
AND(fields=(body), KEYWORD(dog, querypos=2, morphed)))EXPLAIN QUERY ... option format=dot allows displaying the execution tree of a provided full-text query in a hierarchical format suitable for visualization by existing tools, such as https://dreampuf.github.io/GraphvizOnline:
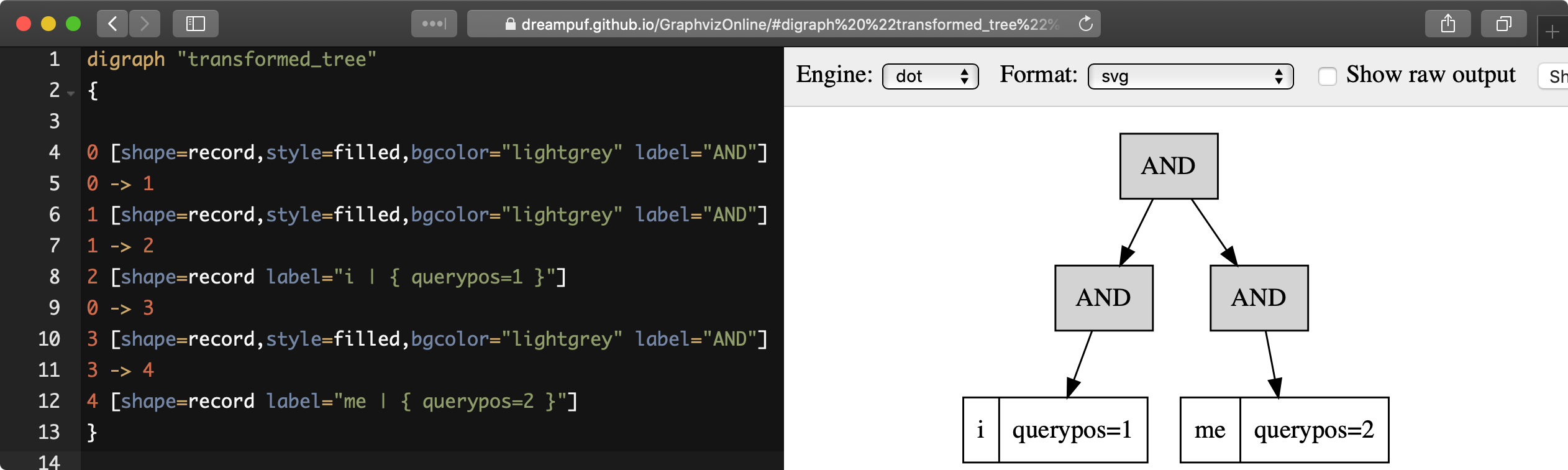
- SQL
EXPLAIN QUERY tbl 'i me' option format=dot\GEXPLAIN QUERY tbl 'i me' option format=dot\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Variable: transformed_tree
Value: digraph "transformed_tree"
{
0 [shape=record,style=filled,bgcolor="lightgrey" label="AND"]
0 -> 1
1 [shape=record,style=filled,bgcolor="lightgrey" label="AND"]
1 -> 2
2 [shape=record label="i | { querypos=1 }"]
0 -> 3
3 [shape=record,style=filled,bgcolor="lightgrey" label="AND"]
3 -> 4
4 [shape=record label="me | { querypos=2 }"]
}When using an expression ranker, it's possible to reveal the values of the calculated factors with the PACKEDFACTORS() function.
The function returns:
- The values of document-level factors (such as bm25, field_mask, doc_word_count)
- A list of each field that generated a hit (including lcs, hit_count, word_count, sum_idf, min_hit_pos, etc.)
- A list of each keyword from the query along with their tf and idf values
These values can be utilized to understand why certain documents receive lower or higher scores in a search or to refine the existing ranking expression.
- SQL
SELECT id, PACKEDFACTORS() FROM test1 WHERE MATCH('test one') OPTION ranker=expr('1')\G id: 1
packedfactors(): bm25=569, bm25a=0.617197, field_mask=2, doc_word_count=2,
field1=(lcs=1, hit_count=2, word_count=2, tf_idf=0.152356,
min_idf=-0.062982, max_idf=0.215338, sum_idf=0.152356, min_hit_pos=4,
min_best_span_pos=4, exact_hit=0, max_window_hits=1, min_gaps=2,
exact_order=1, lccs=1, wlccs=0.215338, atc=-0.003974),
word0=(tf=1, idf=-0.062982),
word1=(tf=1, idf=0.215338)
1 row in set (0.00 sec)