Example of a complex query:
"hello world" @title "example program"~5 @body python -(php|perl) @* codeThe full meaning of this search is:
- Find the words 'hello' and 'world' adjacently in any field in a document;
- Additionally, the same document must also contain the words 'example' and 'program' in the title field, with up to, but not including, 5 words between the words in question; (E.g. "example PHP program" would be matched however "example script to introduce outside data into the correct context for your program" would not because two terms have 5 or more words between them)
- Additionally, the same document must contain the word 'python' in the body field, but not contain either 'php' or 'perl';
- Additionally, the same document must contain the word 'code' in any field.
OR operator precedence is higher than AND, so "looking for cat | dog | mouse" means "looking for ( cat | dog | mouse )" and not "(looking for cat) | dog | mouse".
To understand how a query will be executed, Manticore Search offer query profile tooling for viewing the query tree created by a query expression.
When using SQL statement the full-text query profiling needs to be enabled before running the desired query:
SET profiling =1;
SELECT * FROM test WHERE MATCH('@title abc* @body hey');To view the query tree, we must run SHOW PLAN right after the execution of the query:
SHOW PLAN;The command will return the structure of the executed query. Please note that the 3 statements - SET profiling, the query and SHOW - must run on the same session.
In HTTP, we can just enable "profile":true to get in response the full-text query tree structure.
{
"index":"test",
"profile":true,
"query":
{
"match_phrase": { "_all" : "had grown quite" }
}
}The response will contain a profile object in which we can find a member query.
query property contains the transformed full-text query tree. Each node contains:
type: node type. Can be AND, OR, PHRASE, KEYWORD etc.description: query subtree for this node shown as a string (inSHOW PLANformat)children: child nodes, if anymax_field_pos: maximum position within a field
A keyword node will also provide:
word: transformed keyword.querypos: position of this keyword in a query.excluded: keyword excluded from query.expanded: keyword added by prefix expansion.field_start: keyword must occur at the very start of the field.field_end: keyword must occur at the very end of the field.boost: keyword IDF will be multiplied by this.
- SQL
- HTTP
- PHP
- Python
- javascript
- Java
SET profiling=1;
SELECT * FROM test WHERE MATCH('@title abc* @body hey');
SHOW PLAN \G*************************** 1\. row ***************************
Variable: transformed_tree
Value: AND(
OR(fields=(title), KEYWORD(abcx, querypos=1, expanded), KEYWORD(abcm, querypos=1, expanded)),
AND(fields=(body), KEYWORD(hey, querypos=2)))
1 row in set (0.00 sec)In some cases the evaluated query tree can be rather different from the original one because of expansions and other transformations.
- SQL
- HTTP
- PHP
- Python
- javascript
- Java
SET profiling=1;
SELECT id FROM forum WHERE MATCH('@title way* @content hey') LIMIT 1;
SHOW PLAN;Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
+--------+
| id |
+--------+
| 711651 |
+--------+
1 row in set (0.04 sec)
+------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Variable | Value |
+------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| transformed_tree | AND(
OR(
OR(
AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(wayne, querypos=1, expanded)),
OR(
AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(ways, querypos=1, expanded)),
AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(wayyy, querypos=1, expanded)))),
AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way, querypos=1, expanded)),
OR(fields=(title), KEYWORD(way*, querypos=1, expanded))),
AND(fields=(content), KEYWORD(hey, querypos=2))) |
+------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)The SQL statement EXPLAIN QUERY allows displaying the execution tree of a provided full-text query without running an actual search query on the index.
- SQL
EXPLAIN QUERY index_base '@title running @body dog'\G EXPLAIN QUERY index_base '@title running @body dog'\G
*************************** 1\. row ***************************
Variable: transformed_tree
Value: AND(
OR(
AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(run, querypos=1, morphed)),
AND(fields=(title), KEYWORD(running, querypos=1, morphed))))
AND(fields=(body), KEYWORD(dog, querypos=2, morphed)))EXPLAIN QUERY ... option format=dot allows displaying the execution tree of a provided full-text query in hierarchical format suitable for visualization by existing tools, for example https://dreampuf.github.io/GraphvizOnline :
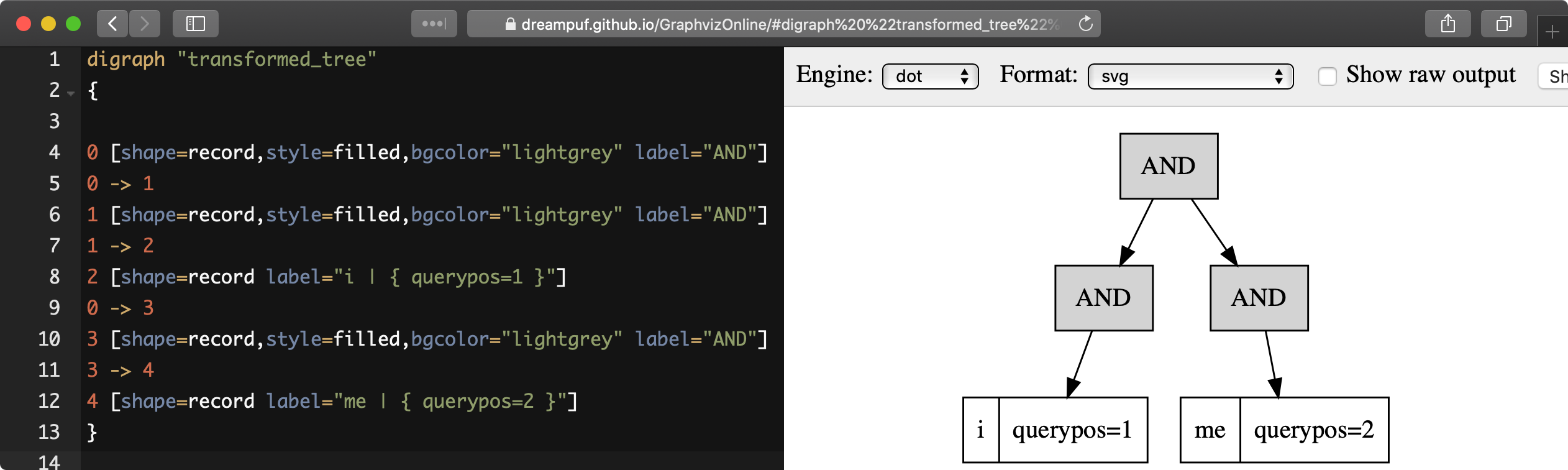
- SQL
EXPLAIN QUERY idx 'i me' option format=dot\GEXPLAIN QUERY idx 'i me' option format=dot\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Variable: transformed_tree
Value: digraph "transformed_tree"
{
0 [shape=record,style=filled,bgcolor="lightgrey" label="AND"]
0 -> 1
1 [shape=record,style=filled,bgcolor="lightgrey" label="AND"]
1 -> 2
2 [shape=record label="i | { querypos=1 }"]
0 -> 3
3 [shape=record,style=filled,bgcolor="lightgrey" label="AND"]
3 -> 4
4 [shape=record label="me | { querypos=2 }"]
}When expression ranker is used, it is possible to expose the values of the calculated factors using PACKEDFACTORS().
The function returns:
- the values of document level factors (like bm25, field_mask, doc_word_count)
- list with each field that returned a hit (like lcs, hit_count, word_count sum_idf, min_hit_pos etc.)
- list with each keyword from the query and their tf and idf values
The values can be used to understand why certain documents get scored lower or higher in a search or to improve the existing ranking expression.
- SQL
SELECT id, PACKEDFACTORS() FROM test1 WHERE MATCH('test one') OPTION ranker=expr('1')\G id: 1
packedfactors(): bm25=569, bm25a=0.617197, field_mask=2, doc_word_count=2,
field1=(lcs=1, hit_count=2, word_count=2, tf_idf=0.152356,
min_idf=-0.062982, max_idf=0.215338, sum_idf=0.152356, min_hit_pos=4,
min_best_span_pos=4, exact_hit=0, max_window_hits=1, min_gaps=2,
exact_order=1, lccs=1, wlccs=0.215338, atc=-0.003974),
word0=(tf=1, idf=-0.062982),
word1=(tf=1, idf=0.215338)
1 row in set (0.00 sec)